文档简介:
(1)Python math 模块:Python 中数学运算常用的函数基本都在 math 模块
import math
print(math.ceil(4.1)) #返回数字的上入整数 print(math.floor(4.9)) #返回数字的下舍整数
print(math.fabs(-10)) #返回数字的绝对值 print(math.sqrt(9)) #返回数字的平方根 print(math.exp(1)) #返回e的x次幂
5 4 10.0 3.0 2.718281828459045
(2)Python随机数
首先import random,使用random()方法即可随机生成一个[0,1)范围内的实数
import random
ran = random.random()
print(ran)
0.4536929444397546
randint()生成一个随机整数
ran = random.randint(1,20)
print(ran)
18
字符串连接:+
a = "Hello " b = "World " print(a + b)
Hello World
重复输出字符串:*
print(a * 3)
Hello Hello Hello
通过索引获取字符串中字符[]
print(a[0])
H
字符串截取[:] 牢记:左闭右开
print(a[1:4])
ell
判断字符串中是否包含给定的字符: in, not in
print('e' in a)
print('e' not in a)
True False
join():以字符作为分隔符,将字符串中所有的元素合并为一个新的字符串
new_str = '-'.join('Hello')
print(new_str)
H-e-l-l-o
字符串单引号、双引号、三引号
print('Hello World!')
print("Hello World!")
转义字符 \
print("The \t is a tab")
print('I\'m going to the movies')
The is a tab I'm going to the movies
三引号让程序员从引号和特殊字符串的泥潭里面解脱出来,自始至终保持一小块字符串的格式是所谓的WYSIWYG(所见即所得)格式的。
print('''I'm going to the movies''')
html = '''
<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>
Friends CGI Demo</TITLE></HEAD>
<BODY><H3>ERROR</H3>
<B>%s</B><P>
<FORM><INPUT TYPE=button VALUE=Back
ONCLICK="window.history.back()"></FORM>
</BODY></HTML>
''' print(html)
I'm going to the movies <HTML><HEAD><TITLE> Friends CGI Demo</TITLE></HEAD> <BODY><H3>ERROR</H3> <B>%s</B><P> <FORM><INPUT TYPE=button VALUE=Back ONCLICK="window.history.back()"></FORM> </BODY></HTML>
声明一个列表,并通过下标或索引获取元素
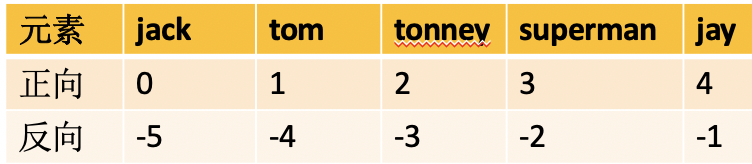
#声明一个列表 names = ['jack','tom','tonney','superman','jay'] #通过下标或索引获取元素 print(names[0])
print(names[1])
jack tom
#获取最后一个元素 print(names[-1])
print(names[len(names)-1])
#获取第一个元素 print(names[-5])
#遍历列表,获取元素 for name in names:
print(name)
#查询names里面有没有superman for name in names: if name == 'superman':
print('有超人') break else:
print('无超人')
#更简单的方法,来查询names里有没有superman if 'superman' in names:
print('有超人') else:
print('无超人')
列表元素添加
#声明一个空列表 girls = [] #append(),末尾追加 girls.append('杨超越')
print(girls)
['杨超越']
#extend(),一次添加多个。把一个列表添加到另一个列表 ,列表合并。 models = ['刘雯','奚梦瑶']
girls.extend(models) #girls = girls + models print(girls)
['杨超越', '刘雯', '奚梦瑶', '刘雯', '奚梦瑶']
#insert():指定位置添加 girls.insert(1,'虞书欣')
print(girls)
列表元素修改,通过下标找到元素,然后用=赋值
fruits = ['apple','pear','香蕉','pineapple','草莓']
print(fruits)
fruits[-1] = 'strawberry' print(fruits)
['apple', 'pear', '香蕉', 'pineapple', '草莓'] ['apple', 'pear', '香蕉', 'pineapple', 'strawberry']
'''
将fruits列表中的‘香蕉’替换为‘banana’
''' for fruit in fruits: if '香蕉' in fruit:
fruit = 'banana' print(fruits) for i in range(len(fruits)): if '香蕉' in fruits[i]:
fruits[i] = 'banana' break print(fruits)
['apple', 'pear', '香蕉', 'pineapple', 'strawberry'] ['apple', 'pear', 'banana', 'pineapple', 'strawberry']
列表元素删除
words = ['cat','hello','pen','pencil','ruler'] del words[0]
print(words)
['hello', 'pen', 'pencil', 'ruler']
words = ['cat','hello','pen','pencil','ruler']
words.remove('cat')
print(words)
['hello', 'pen', 'pencil', 'ruler']
words = ['cat','hello','pen','pencil','ruler']
words.pop(0)
print(words)
['hello', 'pen', 'pencil', 'ruler']
列表切片
-
在Python中处理列表的部分元素,称之为切片。
-
创建切片,可指定要使用的第一个元素和最后一个元素的索引。注意:左闭右开
-
将截取的结果再次存放在一个列表中,所以还是返回列表
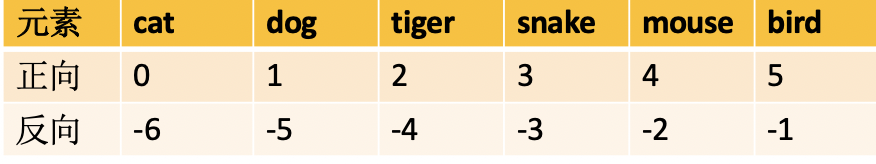
animals = ['cat','dog','tiger','snake','mouse','bird']
print(animals[2:5])
print(animals[-1:])
print(animals[-3:-1])
print(animals[-5:-1:2])
print(animals[::2])
['tiger', 'snake', 'mouse'] ['bird'] ['snake', 'mouse'] ['dog', 'snake'] ['cat', 'tiger', 'mouse']
列表排序
- 随机生成10个不同的整数,并进行排序
'''
需求:生成10个不同的随机整数,并存至列表中
''' import random
random_list = [] for i in range(10):
ran = random.randint(1,20) if ran not in random_list:
random_list.append(ran)
print(random_list)
[8, 14, 12, 20, 13, 10, 15, 6]
上述代码存在什么问题吗?
import random
random_list = []
i = 0 while i < 10:
ran = random.randint(1,20) if ran not in random_list:
random_list.append(ran)
i+=1 print(random_list)
#默认升序 new_list = sorted(random_list)
print(new_list) #降序 new_list = sorted(random_list,reverse =True)
print(new_list)
tuple1 = ()
print(type(tuple1))
<class 'tuple'>
tuple2 = ('hello')
print(type(tuple2))
<class 'str'>
注意:元组中只有一个元素时,需要在后面加逗号!
tuple3 = ('hello',)
print(type(tuple3))
<class 'tuple'>
元组不能修改,所以不存在往元组里加入元素。
那作为容器的元组,如何存放元素?
import random
random_list = [] for i in range(10):
ran = random.randint(1,20)
random_list.append(ran)
print(random_list)
random_tuple = tuple(random_list)
print(random_tuple)
[14, 4, 2, 14, 13, 4, 12, 3, 7, 9] (14, 4, 2, 14, 13, 4, 12, 3, 7, 9)
元组访问
print(random_tuple)
print(random_tuple[0])
print(random_tuple[-1])
print(random_tuple[1:-3])
print(random_tuple[::-1])
元组的修改:
t1 = (1,2,3)+(4,5)
print(t1)
(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
t2 = (1,2) * 2 print(t2)
(1, 2, 1, 2)
元组的一些函数:
print(max(random_tuple))
print(min(random_tuple))
print(sum(random_tuple))
print(len(random_tuple))
14 2 82 10
#定义一个空字典 dict1 = {}
dict2 = {'name':'杨超越','weight':45,'age':25}
print(dict2['name'])
杨超越
#list可以转成字典,但前提是列表中元素都要成对出现 dict3 = dict([('name','杨超越'),('weight',45)])
print(dict3)
dict4 = {}
dict4['name'] = '虞书欣' dict4['weight'] = 43 print(dict4)
{'name': '虞书欣', 'weight': 43}
dict4['weight'] = 44 print(dict4)
{'name': '虞书欣', 'weight': 44}
#字典里的函数 items() keys() values() dict5 = {'杨超越':165,'虞书欣':166,'上官喜爱':164}
print(dict5.items()) for key,value in dict5.items(): if value > 165:
print(key)
dict_items([('杨超越', 165), ('虞书欣', 166), ('上官喜爱', 164)])
虞书欣
#values() 取出字典中所有的值,保存到列表中 results = dict5.values()
print(results)
dict_values([165, 166, 164])
#求小姐姐的平均身高 heights = dict5.values()
print(heights)
total = sum(heights)
avg = total/len(heights)
print(avg)
dict_values([165, 166, 164]) 165.0
names = dict5.keys() print(names)
dict_keys(['杨超越', '虞书欣', '上官喜爱'])
#print(dict5['赵小棠']) #若不存在“赵小棠”,会报错KeyError print(dict5.get('赵小棠'))
print(dict5.get('赵小棠',170)) #如果能够取到值,则返回字典中的值,否则返回默认值170
None 170
dict6 = {'杨超越':165,'虞书欣':166,'上官喜爱':164} del dict6['杨超越']
print(dict6)
{'虞书欣': 166, '上官喜爱': 164}
result = dict6.pop('虞书欣')
print(result)
print(dict6)
166
{'上官喜爱': 164}
定义一个类Animals:
(1)init()定义构造函数,与其他面向对象语言不同的是,Python语言中,会明确地把代表自身实例的self作为第一个参数传入
(2)创建一个实例化对象 cat,init()方法接收参数
(3)使用点号 . 来访问对象的属性。
class Animal: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name
print('动物名称实例化') def eat(self): print(self.name +'要吃东西啦!') def drink(self): print(self.name +'要喝水啦!')
cat = Animal('miaomiao')
print(cat.name)
cat.eat()
cat.drink()
class Person: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name print ('调用父类构造函数')
def eat(self): print('调用父类方法') class Student(Person): # 定义子类 def __init__
(self): print ('调用子类构造方法') def study(self): print('调用子类方法')
s = Student() # 实例化子类 s.study() # 调用子类的方法 s.eat() # 调用父类方法
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人阅读和编写。
json.dumps 用于将 Python 对象编码成 JSON 字符串。
import json
data = [ { 'b' : 2, 'd' : 4, 'a' : 1, 'c' : 3, 'e' : 5 } ]
json = json.dumps(data)
print(json)
[{"b": 2, "d": 4, "a": 1, "c": 3, "e": 5}]
为了提高可读性,dumps方法提供了一些可选的参数。
sort_keys=True表示按照字典排序(a到z)输出。
indent参数,代表缩进的位数
separators参数的作用是去掉,和:后面的空格,传输过程中数据越精简越好
import json
data = [ { 'b' : 2, 'd' : 4, 'a' : 1, 'c' : 3, 'e' : 5 } ]
json = json.dumps(data, sort_keys=True, indent=4,separators=(',', ':'))
print(json)
[
{
"a":1,
"b":2,
"c":3,
"d":4,
"e":5
}
]
json.loads 用于解码 JSON 数据。该函数返回 Python 字段的数据类型。
import json
jsonData = '{"a":1,"b":2,"c":3,"d":4,"e":5}' text = json.loads(jsonData) #将string转换为dict print(text)
{'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4, 'e': 5}
try:
fh = open("/home/aistudio1/data/testfile01.txt", "w")
fh.write("这是一个测试文件,用于测试异常!!") except IOError:
print('Error: 没有找到文件或读取文件失败') else: print ('内容写入文件成功')
fh.close()
Error: 没有找到文件或读取文件失败
finally中的内容,退出try时总会执行
try:
f = open("/home/aistudio/data/testfile02.txt", "w")
f.write("这是一个测试文件,用于测试异常!!") finally:
print('关闭文件')
f.close()
关闭文件
f = open("work/test.txt",'w') #变量名=open(文件路径和文件名,打开模式) 模式:w:写,r:只写;a:追加写 f.write("hello")
f.write("\npython")
f.close()
f = open("work/test.txt",'r') #变量名=open(文件路径和文件名,打开模式) 模式:w:写,r:只写;
a:追加写 # print(f.read()) #f.read():从文件中读入整个文件内容,结果为字符串 # print(f.readline()
) #f.readline():从文件中读入一行内容,结果为字符串 print(f.readlines()) #f.readlines():
从文件中读取所有行,以每行元素形成一个列表 f.close()
['hello\n', 'python']
使用open()函数打开的文件对象,必须手动进行关闭,Python 垃圾回收机制无法自动回收打开文件所占用的资源。
因此,推荐以下写法:
with open("work/test.txt",'a') as f:
f.write("PadddlePaddle")
f.write("\nokokok")
!ls /home
aistudio
!ls ./
ls -l
!pwd
cp :复制文件或目录
!cp test.txt ./test_copy.txt
mv:移动文件与目录,或修改文件与目录的名称
!mv /home/aistudio/work/test_copy.txt /home/aistudio/data/
rm :移除文件或目录
!rm /home/aistudio/data/test_copy.txt
很多大型文件或者数据从服务器上传或者下载的时候都需要打包和压缩解压,这时候知道压缩和解压的各种命令是很有必要的。
常见的压缩文件后缀名有.tar.gz,.gz,和.zip,下面来看看在Linux上它们分别的解压和压缩命令。
#会将文件压缩为文件 test.txt.gz,原来的文件则没有了,解压缩也一样 !gzip /home/aistudio/work/test.txt
!gzip -d /home/aistudio/test.gz
!tar -zcvf /home/aistudio/work/test.tar.gz /home/aistudio/work/test.txt
!tar -zxvf /home/aistudio/work/test.tar.gz
!zip -r /home/aistudio/work/test.zip /home/aistudio/work/test.txt
!unzip /home/aistudio/work/test.zip






